Highly dispersed carbon nanotubes
What are carbon nanotubes (CNTs)?
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are nanostructures consisting of carbon atoms bound together in hexagonal graphene sheets and wound into a tube-like structure.
This unique structure gives them outstanding electrical and thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, and they are attracting attention as a next-generation, highly functional material.In particular, it is expected to be applied in a wide range of fields, including conductive materials for electronic components, electromagnetic wave shielding materials, and heat-generating sheets.
In recent years, mass production of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) has been improved, and stable supply and cost performance have been realized.
Main physical properties of MWCNTs
Electrical conductivity |
10⁴~10⁵ S/m (about 1/100~1/10 of metallic copper) |
|---|---|
Thermal conductivity |
3,000 W/m-K (about 5 times that of copper) |
Tensile strength |
50 to 150 GPa (about 50 times that of steel) |
Specific gravity |
~1.3 to 1.4 g/cm³ (lighter than aluminum) |
Aspect Ratio |
1,000 or more (Highly efficient electrical conductivity) |
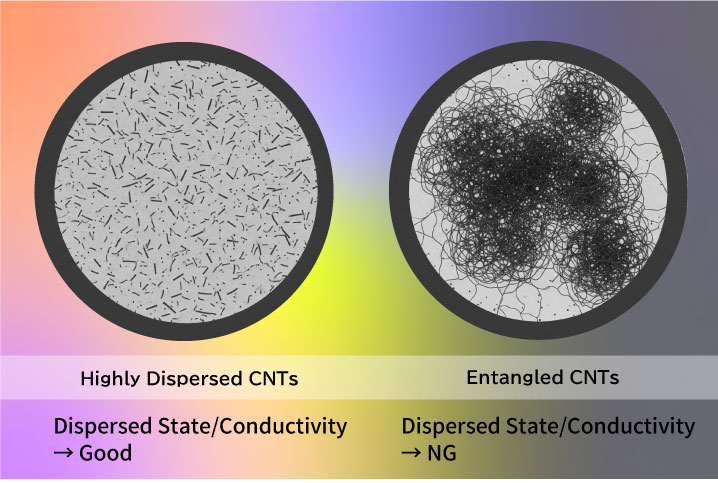
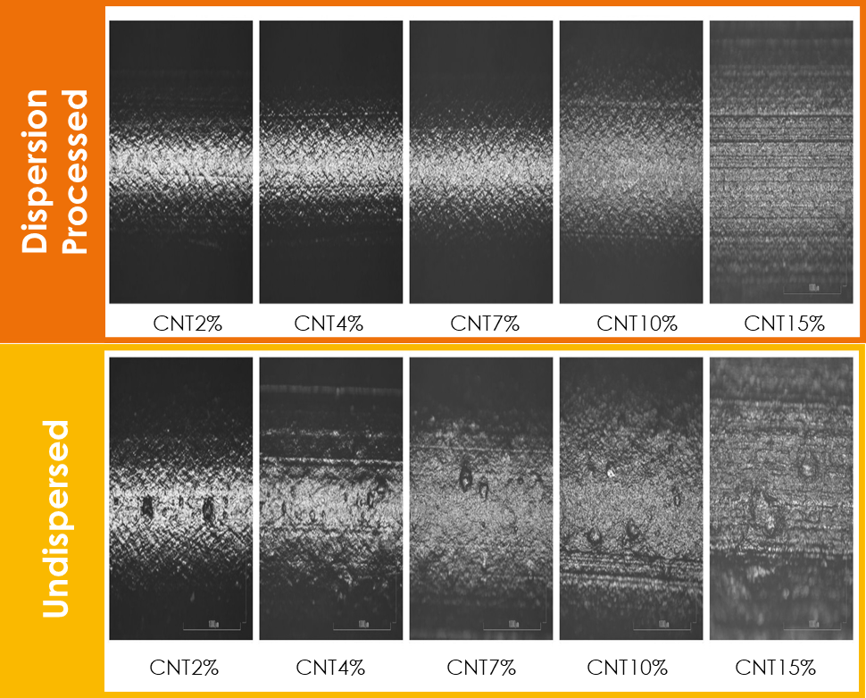
Despite these excellent properties, MWCNTs are prone to aggregation due to their high aspect ratio.Properly breaking up agglomerates and dispersing them uniformly can maximize the original performance of MWCNTs.
About Moriroku Technology

Moriroku has been providing "highly dispersed CNT masterbatches" with no agglomerates by utilizing its proprietary dispersion technology. This is expected to provide uniform conductivity to resins and rubbers, electromagnetic shielding, and also to improve heat generation performance.
We will continue to support our customers' product development by responding to diverse applications.
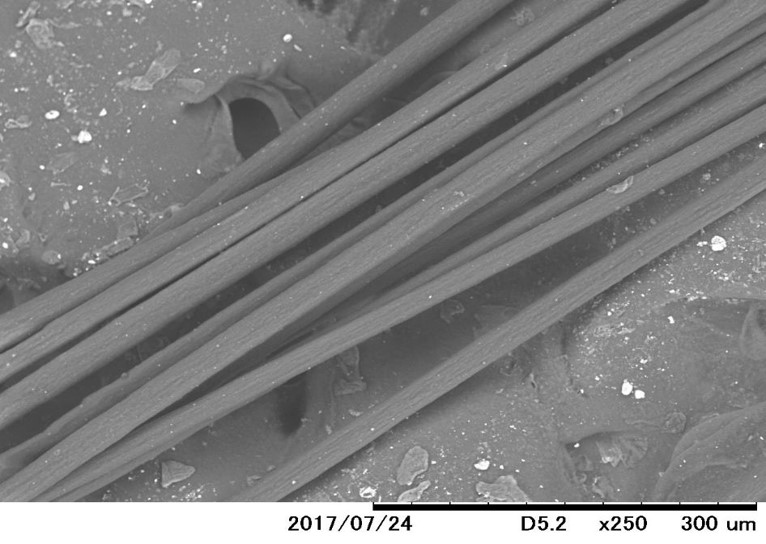
Micrograph of CNT MB/pellet surface
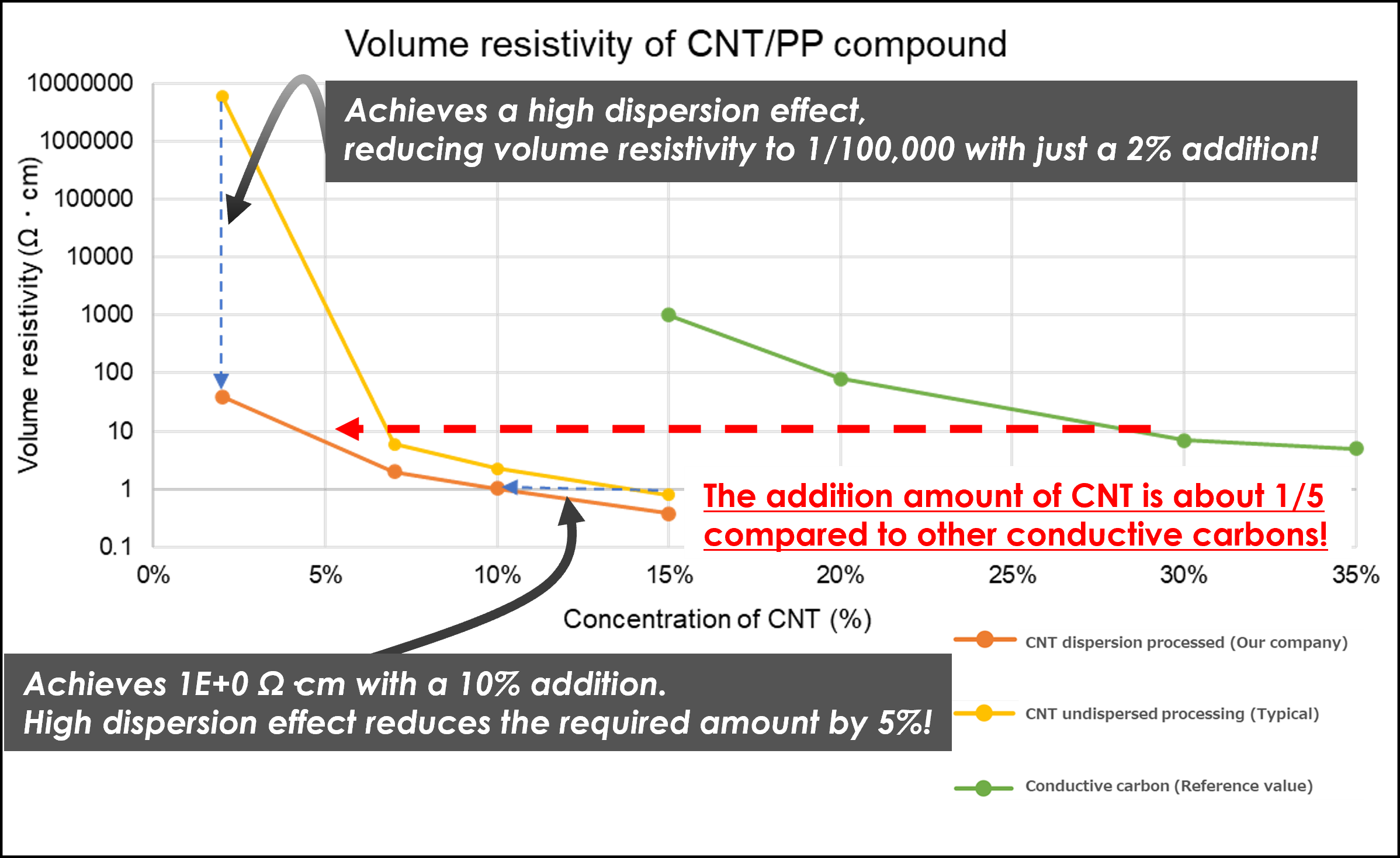
CNT/PP Compound Volume Resistivity
Main Features
-
CNTs can be blended with a wide range of resins such as general-purpose resins, engineering plastics, and elastomers.
-
CNTs can be blended with silicone rubber, NBR, EPDM, and other rubbers.
-
Easy to handle during molding by preventing re-agglomeration of CNTs.
-
Easy to handle when molding. ・CNTs can be diluted by general biaxial extrusion.
-
High conductivity can be achieved by adding a small amount of CNTs, so resin properties are not degraded.
-
No contamination of the work environment or color migration due to lack of carbon.
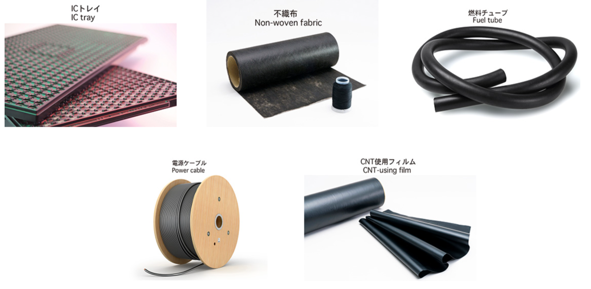
Applications and Uses
Why Moriroku’s High-Dispersion Carbon Masterbatch Is the Material of Choice
-
High conductivity with minimal additive content → Maintains softness
-
Excellent dispersion and uniformity → Effective electromagnetic shielding
Moriroku’s high-dispersion carbon masterbatch is a next-generation material that simultaneously delivers softness, conductivity, and lightweight performance—qualities that are often difficult to achieve together.
It is expected to play a key role in future-focused fields such as next-generation mobility, IoT, healthcare, and smart textiles.
-
Connecting Electricity with Flexibility: A New Option in Conductive Rubber
Moriroku has successfully unlocked the full potential of carbon nanotubes (CNTs)—renowned for their exceptional conductivity—through its proprietary high-dispersion technology. This innovation enables superior conductivity with significantly lower additive content, while preserving the inherent softness of rubber materials.

-
A Breakthrough Material for the Future! The Potential of Carbon Nanotubes and Moriroku’s Innovative Technology
Using Moriroku’s proprietary processing method, tangled, ball-like multi-walled CNTs are disentangled and transformed into a non-agglomerated state. These dispersed CNTs are then uniformly distributed within resin and offered as pelletized high-dispersion CNT masterbatch.